The industry uses reactors to mix reacting components. In order to ensure an ideal reaction it is often necessary to maintain a certain temperature. The reaction rate and, consequently, the heat release (absorption) rate in the reactor depends on the mixture temperature. This paper describes a nonlinear model of a perfect mixing reactor, taking into account the temperature dependence of reactivity. The simulation was performed by REPEAT software. The resulting model makes it possible to determine the temperature and concentration of substance at the reactor outlet. Equipping a model with a PI controller made it possible to control the mixture temperature within a suitable range.
Input information for model building
This article describes a simulation of a perfect mixing reactor ![]() in REPEAT software.
in REPEAT software.
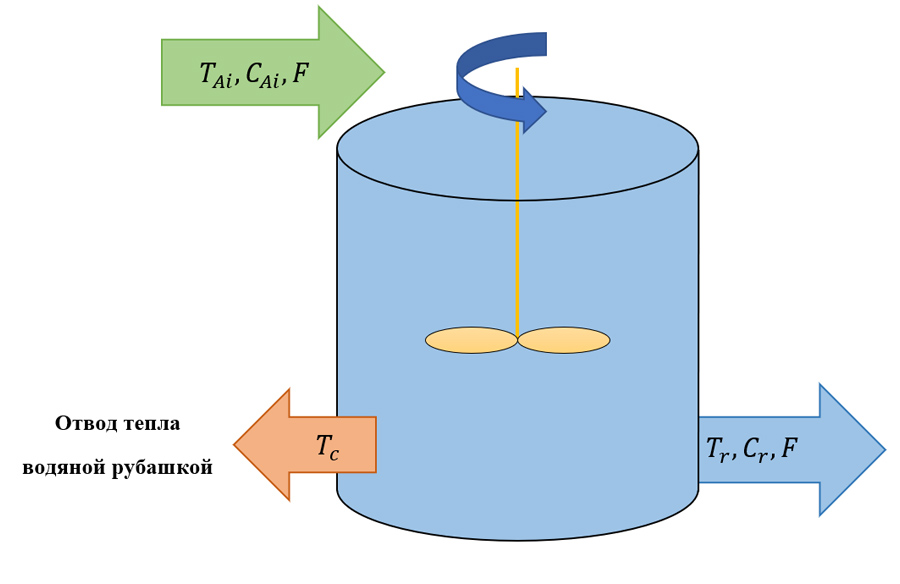
Perfect mixing (full mixing) reactors are devices which instantly and uniformly mix the flows of reactants throughout the reaction volume. It means that the composition and temperature of the reaction mixture in such device can be assumed to be the same throughout its entire volume. A circuit diagram of a simulated perfect mixing device is shown in Figure 1.
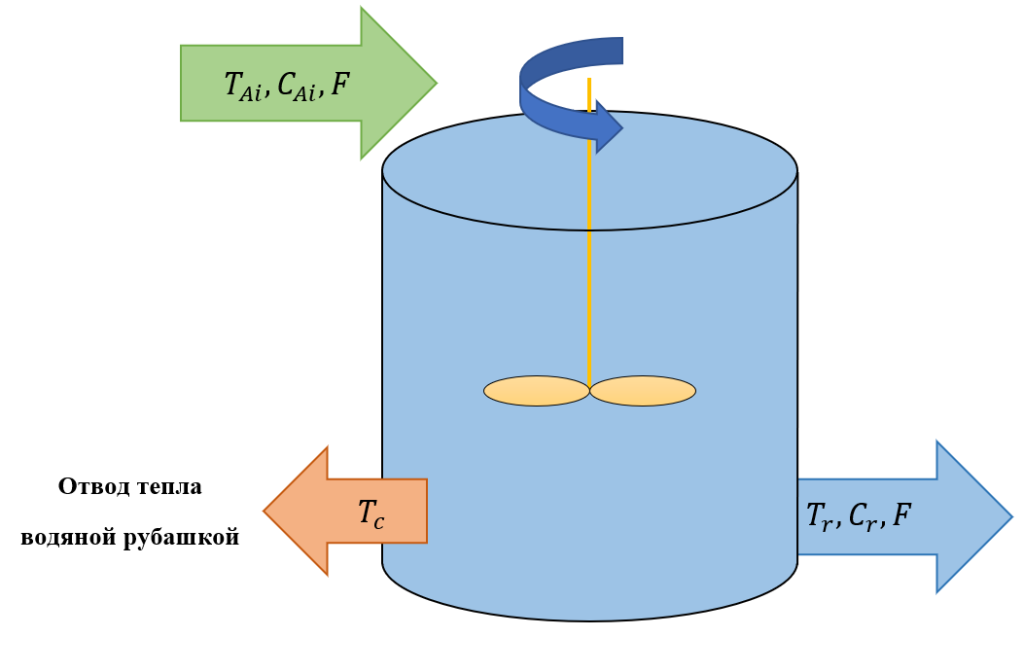
Отвод тепла водяной рубашкой -Heat removal by water jacket
Figure 1. Circuit diagram of a perfect mixing reactor
The following designations are used in this figure:
![]() – inlet flow temperature;
– inlet flow temperature;
![]() – outgoing mixture temperature;
– outgoing mixture temperature;
![]() – cooling medium temperature;
– cooling medium temperature;
![]() – concentration of substance A in incoming flow;
– concentration of substance A in incoming flow;
![]() – concentration of substance A in outgoing mixture;
– concentration of substance A in outgoing mixture;
![]() – volumetric flow rate of incoming flow.
– volumetric flow rate of incoming flow.
Applications of perfect mixing reactors are listed below:
Applications:
- microbiological industry;
- fermentation;
- water treatment systems.
Manufacturing:
- reagents;
- organic dyes;
- pharmaceuticals.
Simulation of perfect mixing reactor
Let’s write down the molar balance of the components:
![]()
where ![]() is the number of moles of a component;
is the number of moles of a component;
![]() – a generation rate.
– a generation rate.
Let us transform the resulting equation:
![]()
Since ![]() :
:
![]()
Divide both parts into ![]() and obtain the differential equation of change in substance concentration:
and obtain the differential equation of change in substance concentration:
![]()
Let’s write down the energy balance equation:
![]()
Where ![]() is the heat released in the reaction per unit of time;
is the heat released in the reaction per unit of time;
![]() is the rate of heat removal by the cooling system.
is the rate of heat removal by the cooling system.
Since ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
![]()
Let’s divide both parts into ![]() and get the differential equation of the change in the reactor mixture output temperature:
and get the differential equation of the change in the reactor mixture output temperature:
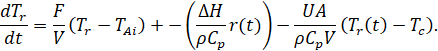
Thus, a continuous mixing reactor with a cooling medium can be described by the following differential equations system:
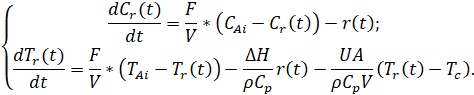
where:
![]() – concentration of substance A in outgoing mixture;
– concentration of substance A in outgoing mixture;
![]() – volume flow rate of incoming flow;
– volume flow rate of incoming flow;
![]() – volume of reactor mixture;
– volume of reactor mixture;
![]() – concentration of substance A in incoming flow;
– concentration of substance A in incoming flow;
![]() – Arrhenius equation;
– Arrhenius equation;
![]() – outgoing mixture temperature;
– outgoing mixture temperature;
![]() – inlet flow temperature;
– inlet flow temperature;
![]() – Boltzmann constant;
– Boltzmann constant;
![]() – heat released in reaction per mole;
– heat released in reaction per mole;
![]() – density of reactor mixture;
– density of reactor mixture;
![]() – heat capacity of reactor mixture;
– heat capacity of reactor mixture;
![]() – activation energy per mole;
– activation energy per mole;
![]() – pre-exponential non-thermal factor;
– pre-exponential non-thermal factor;
![]() – total heat transfer factor multiplied by tank area;
– total heat transfer factor multiplied by tank area;
![]() – cooling medium temperature.
– cooling medium temperature.
Let’s build the reactor model in REPEAT software using the basic blocks (see Figure 2) according to the differential equations above.
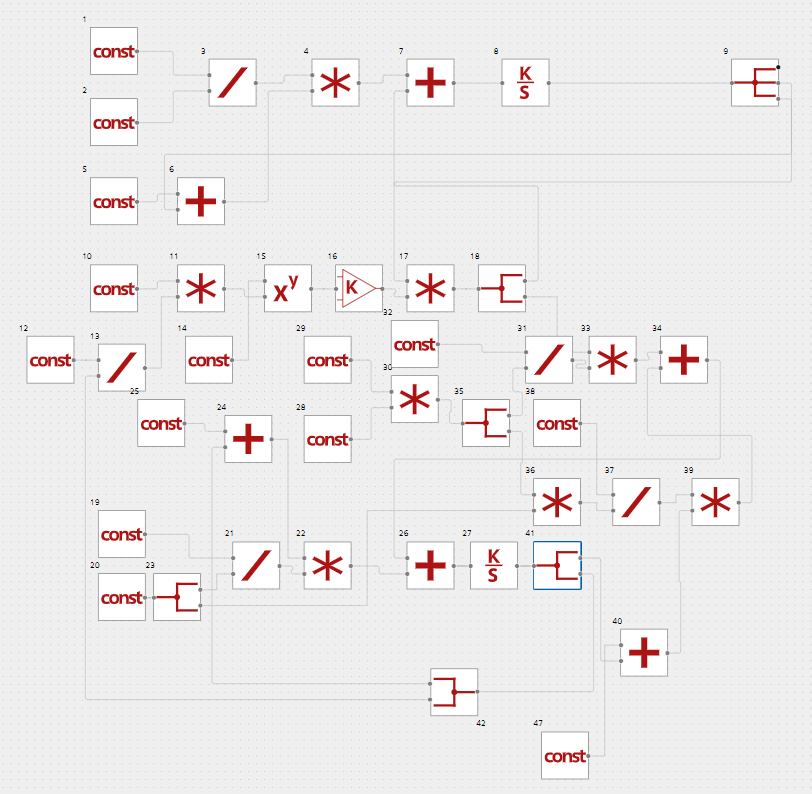
Figure 2. Nonlinear perfect mixing reactor model in REPEAT software
The input data are shown below (see Table 1).
Table 1 Initial data
|
Parameter |
Unit of measurement |
Values used for model debugging |
|
Volume flow rate of incoming flow, |
|
1 |
|
Volume of reactor mixture, |
|
1 |
|
Concentration of substance A in incoming flow, |
|
10 |
|
Incoming flow temperature, |
|
300 |
|
Boltzmann constant, |
|
1.985875 |
|
Heat released in reaction per mole, |
|
-5960 |
|
Density of reactor mixture, |
|
1000 |
|
Heat capacity of reactor mixture, |
|
0.5 |
|
Activation energy per mole, |
|
11843 |
|
Pre-exponential non-thermal factor, |
|
34930800 |
|
Total heat transfer factor multiplied by tank area, |
|
150 |
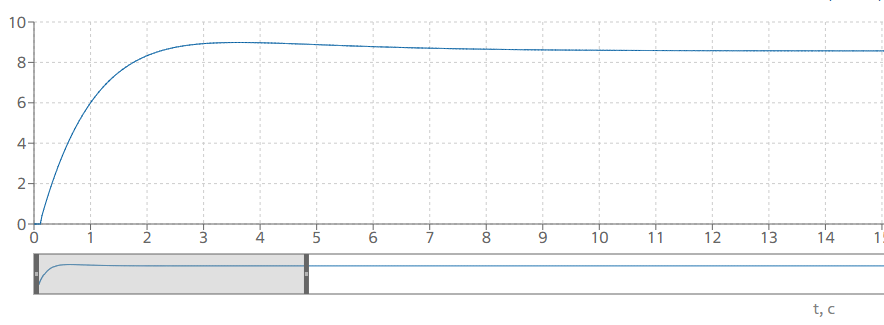
Figure 3. Transient process of establishing the concentration of substance A at the outlet of block No. 8
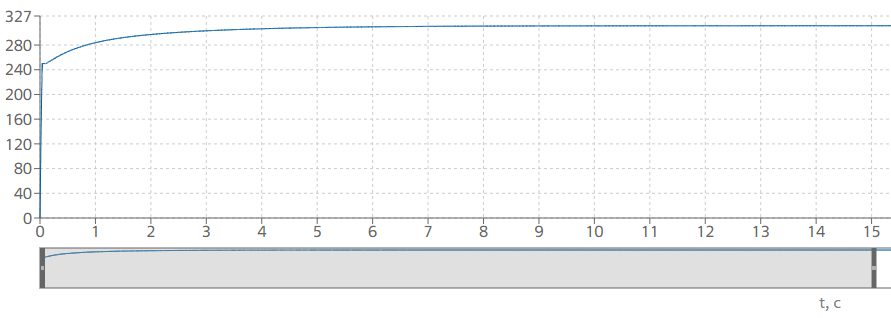
Figure 4. Transient process of establishing the temperature of substance A at the outlet of block No. 27
Adding of a PI controller
In order to control the concentration of substances and to improve the quality of transient process it is necessary to add a PI controller. The diagram with an added controller (block No. 45) is shown in Figure 5.
Table 2. Parameters of PI controller
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
|
-15 |
|
|
0.1 |
Adding of a limiter
In fact, the diagram should be additionally equipped with a limiter due to the need to limit the cooling medium temperature, since the PI controller will change it until the concentration reaches a required value, if possible. In the diagram in Figure 5 the limiter is represented as block No. 44.
The upper limit is the temperature at PMR inlet with a certain margin selected by the user.
The lower limit is a minimum possible temperature of the cooling system cooling medium.
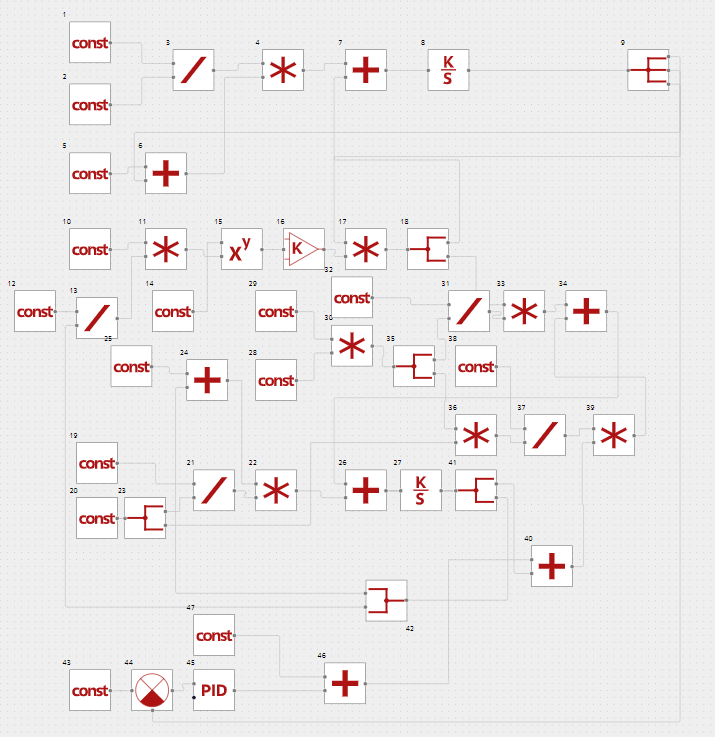
Figure 5. Nonlinear model of perfect mixing reactor with a PI controller (block No. 45) of substance concentration and a limiter (block No. 44)
Simulation results
As a result of simulation of a perfect mixing reactor in REPEAT software, the following calculations of temperature and concentration values are obtained:
![]()
![]()
In turn, the theoretically calculated results are:
![]()
![]()
Thus, the simulation error is less than 1%, which is quite acceptable for this type of simulation. The performance of the perfect mixing reactor model fully corresponds to the expected results. The obtained values make it possible to verify that REPEAT software allows to perform calculations for this type of industrial plants with a required accuracy.